Getting Started with FIDO Server by Worldline
Prerequisites
You need to keep your client_id and secret_id that was sent to you by mail.
If you lost your secret_id, please contact us to generate a new one for you.
There is two types of credentials with different scope. The firsts credentials you received are for the administrative scope, to manage your relying parties servers. You have to use these firsts credentials to create a relying party via API, and in response you will received second credentials related to your relying party with "service" scope that will enable you to configure it and handle your users via API.
These credentials are needed for all interactions with the Fido Server by Worldline.
You also need the audience to access generate bearer tokens.
OAuth2 Server URL : https://access.fido.worldline-solutions.com
Audience : https://my-wafl-api-gateway-6glqflxv.ew.gateway.dev - to update
API access and authentication
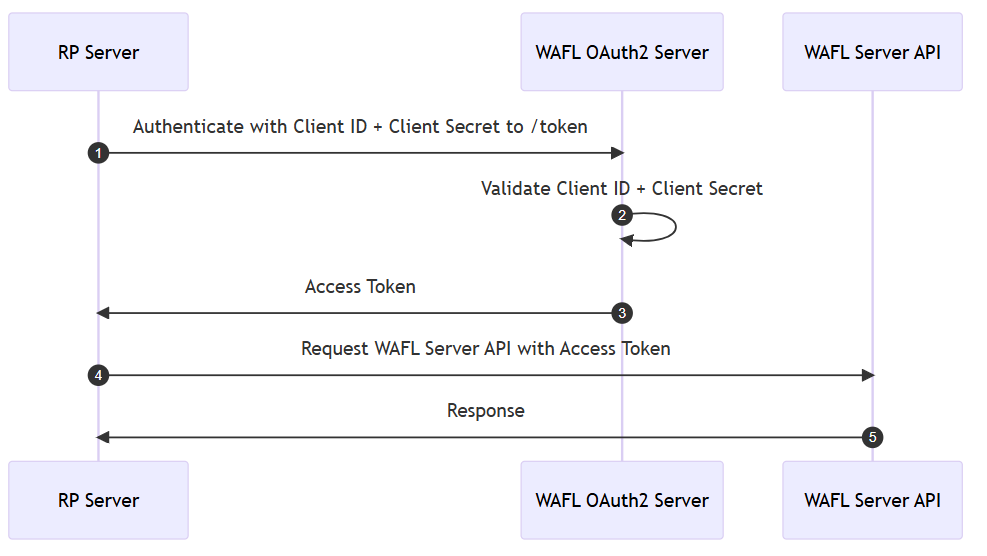
The FIDO Server by Worldline (also called WAFL Server) API uses the OAuth Client Credentials Flow to authenticate API calls.
Request tokens
Example using curl
curl --request POST \
--url 'https://access.fido.dev.worldline-solutions.com/oauth2/token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--header 'Authorization: Basic Base64Encode(concat('client_id', ':', 'client_secret'))' \
--data 'grant_type=client_credentials' \
--data 'audience=https://my-wafl-api-gateway-206w9c7e.ew.gateway.dev'Parameters
- grant_type : set this to your "client_credentials"
- audience : the audiance for the token (see the prerequisites)
Response
If all goes well, you'll receive an HTTP 200 response with a payload containing access_token, and expires_in values:
{
"access_token": "eyJz93a...k4laUWw",
"expires_in": 3600
}Access token lifetime
The lifetime of a token is set to 3600 seconds
Use the Worldline FIDO Server APIs
Declare your relying party server
Once you received your credentials by mail with the "admin" scope, you can declare your relying party server with the admin/relying-parties API, where you give the name of your relying party, and get the credentials with the "service" scope that you can configure in your relying party server to use the FIDO authentication service.
You also have to declare the origins of your relying party application with the admin/relying-parties/{id}/origins API.
Enable your users to register
You can use our Browser SDK to facilitate the integration of FIDO protocol into your web application and use the browser APIs.
The registration is a two steps action as it contains an initiation step to generate the challenge that will be used by the authenticator for cryptographic operations.
In the initiation step your relying party gives information about the registration like the username, friendlyName and authenticator properties. The Worldline FIDO server respond with a challenge to give to the authenticator.
The attestationBlob, response of the authenticator, is passed through the finalization step so that the Fido server complete the registration.
Enable your users to authenticate
The authentication is also a two steps action as it contains an initiation step to generate the challenge that will be used by the authenticator for cryptographic operations.
The initiation step is where your relying party informs the server for which user you want to do an authentication. The response contains the challenge on which the authenticator will have to make cryptographic operations.
The result of these operations is passed through the finalization step in the assertionBlob where the Fido Server will do the authentication.
Manage your users
Once your users are registered, you can list their authenticators, update the friendlyName of an authenticator (for the user to better identify his authenticator) and delete them via the /users APIs.