External RBA
VERSION 26R1 - last update Sept. 18 2025
This specification describes the features proposed by the module WL Authentication Process Management (APM) to process a Risk Based Authentication solution for 3D-Secure platform.
1 Overview
With the enforcement of PSD2, article 97 requires that “Payment Service Providers to authenticate a user when they:
- access an online payment account,
- initiate an electronic payment transaction,
- or carry out any action through a remote channel that may imply a risk of payment fraud”.
This new regulation will lead to an increase in Strong Customer Authentication. In order to provide a better user experience and to lower costs due to Strong Authentication, the Bank can choose a Risk Based Authentication (RBA). RBA is recommended by many regulations (PSD2) and schemes under the EMV 3DS 2.1 protocol.
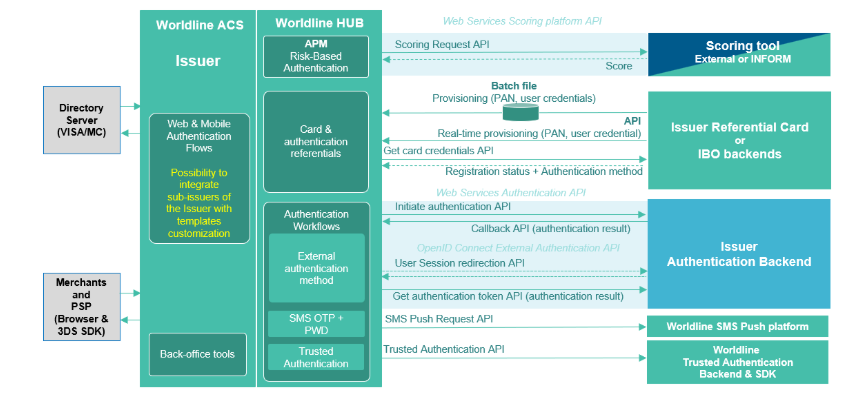
WL APM is a functional extension of the ACS. New modules are added to be able to assess the risk of transactions. Thanks to the transaction risk analysis (TRA), the Bank can decide either to approve the authentication without SCA (frictionless flow), or ask for SCA (Challenge flow), or decline transaction if the risk is too high.
WL APM main goals are to:
- Check exemptions (RTS and others) and determine the right authentication workflow to process,
- Implement RBA for payment and non-payment flows,
- Manage authentication workflow for card based payments (3DS transactions) as well as PSD2 Access to Account use cases (PIS, AIS).
- Propose a bank extranet which functionalities are included in the ACS back-office.
WL APM is agnostic of any scoring platform. Therefore, RBA scoring can be done by Worldline Solution (Inform Riskshield), DS, Issuer Bank or by an external scoring tool.
WL APM is a modular solution which can process RBA and SCA for 3DS Secure flows.
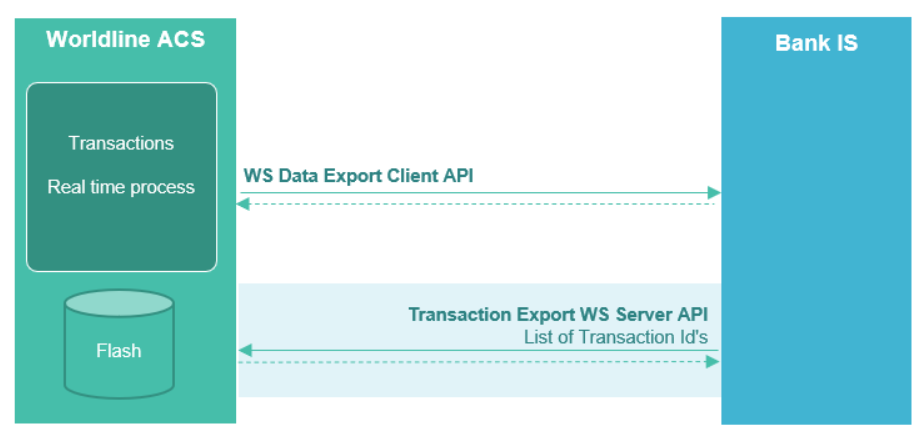
Figure 1 : Overview of WL APM functional architecture
2 Functional description
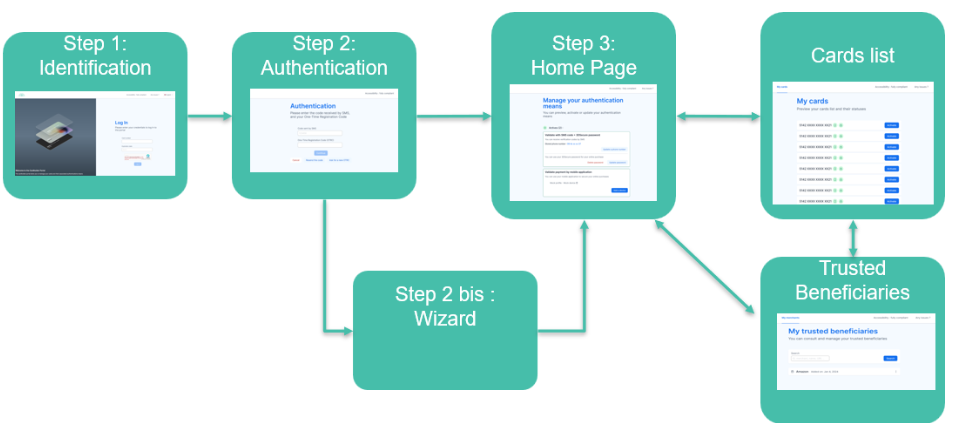
During the initialization of an authentication request, WL ACS is in charge of:
- Identifying the cardholder who has to be authenticated,
- Checking the status of the cardholder,
- Retrieving all the authentication methods available for the cardholder,
- Providing this information to the Service Provider.
WL ACS also includes an additional module, the APM- RBA rules engine, which covers the following complementary features:
- Check Standard Fraud prevention lists (e.g. black lists, white lists, ...),
- Take into account fraud score and recommendation from external platform (DS, merchants, scoring platform, ...)
- Apply Rules (From Bank, Scheme or regulatory framework) to make a decision,
- Provide a Decision to the Service Provider.
Then, the Service Provider is able to make a decision and decide which authentication process to trigger:
- Frictionless: acceptation of the authentication without any authentication action asked to the cardholder
- Strong Customer Authentication: challenge asked to the cardholder
- Decline: refusal of the authentication
Figure 2: Overview of WL APM decision process
2.1 Rules Engine
2.1.1 Workflow
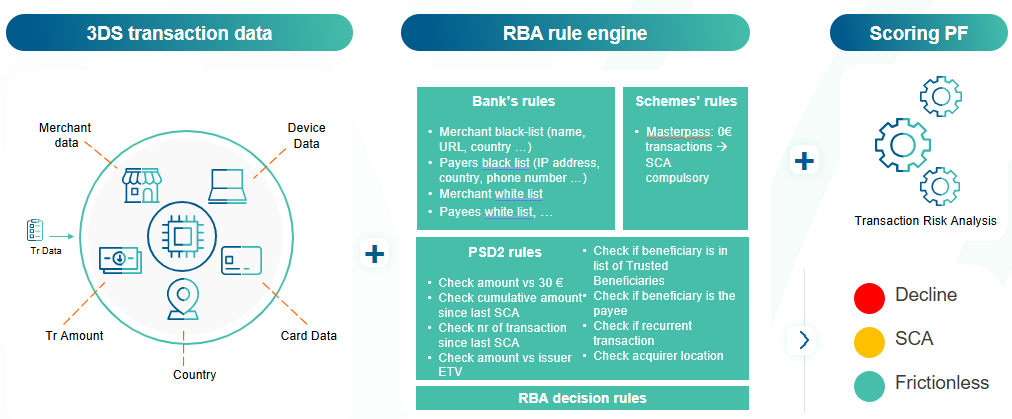
The WL APM rules engine is a module which can apply specific rules, in a defined sequential order to establish a SCA decision.
The decision can take 3 results:
- Frictionless : no authentication requested for the transaction,
- SCA : Strong Customer authentication must be done, in this case strong authentication means available will be provided also to Service Provide
- Decline: the transaction is too risky and must be declined.
WL APM provides a predefined standard set of rules. Then, the Bank chooses which rules or set of rules has to be activated depending on its strategy.
The rules list and the scheduling are defined by the Bank. It can be different depending on the use case (3DS, e-banking, Access to Account…).
Figure 3: Overview of WL APM RBA Rules engine
Categories of rules
The rules engine can manage rules in part or in whole. It allows setting up:
- The bank's own rules
- The rules of the schemes
- RTS exemptions (optional if managed on another bank system)
- The rules related to the score
- Bank specific rules
- Blacklist of users, countries (user IP), phones, merchants
- White list of users
- Merchant pivot amount: list of merchants for whom strong authentication is mandatory above a defined threshold
- Scheme rules
- ID&V
- VPP
- BIN Attack
- RTS Exemption Rules
- Low value transactions (Amount < 30 € and cumulative amount of < 100 € or 5 consecutive frictionless transactions)
- Analysis of the risks related to the transaction (amount between €30 and ETV and risk analysis)
- Trusted beneficiaries
- Secure Corporate
- Rules related to the score:
- Consideration of the recommendation of the scoring platform (frictionless, SCA, decline)
- Interpretation of the score provided (value of the score + recommendation):
- Either by the scoring platform
- or by the directory server
- Fallback
- Interpretation of the score provided (value of the score + recommendation):
- Consideration of the recommendation of the scoring platform (frictionless, SCA, decline)
WL APM RBA parameters
Bank can choose, for example:
- To activate or deactivate the WL APM RBA process
- To activate or deactivate the call to the external Scoring platform
- To take into account or ignore the scoring and recommendation from Directory Server
- To take into account or ignore the scoring and recommendation from external Scoring platform
- To define which scoring is most valuable between Scheme or external platform
- To bypass the score request for a Scheme
- To bypass the score request for virtual Cards
- Value of threshold amount or threshold score
- To activate or deactivate a rule
- To change rule order (switch ordinal of two rules).
- etc.
A new tool, called "Rules Creator", also allows for the creation and management of APM rules entirely independently via the Back-Office (cf. Back-Office User's guide).
In case of technical error or unavailability of the rules engine, it will answer back to the authentication workflow that a SCA has to be triggered.
Moreover, not to slow down the authentication process, a timer can be configured (e.g. DS asks to answer within 5 seconds on Areq/Ares message).
2.1.2 Definition of rules
2.1.2.1 Criterion
Transaction Data used as criterion in rules Engine are:
- Amount of the transaction (converted in Bank's currency),
- Score of the transaction
- Provided by Scheme,
- Provided by External Scoring Platform,
- Provided by Issuer
- SCA recommendation
- Provided by Scheme,
- Provided by External Scoring Platform,
- Provided by Issuer
- Provided by Merchant
- Cumulative amount of consecutive frictionless transactions,
- Number of consecutive frictionless transactions,
- Threshold
- ETV level amount (see § 6.1)
- Frictionless amount threshold (30 EUR as defined by PSD2)
- Minimum Score threshold
- Maximum Score threshold
- Specific Bank thresholds
- Merchant Identity (Name)
- Merchant inclusion in Issuer’s List Merchant
- Merchant country code
- Acquirer country code
- MCC includes in travel industry list (cf. Appendices)
- Protocol version
- Scheme
- Brand
- Secure corporate payment flag
- Recurring and Instalment flag (1st transaction or a recurring n transaction)
- 3RI flag
- 3RI use case based on threeRIInd value
- Message Category value (Payment / Non-Payment / 3RI)
- threeDSRequestorChallengeInd
- threeDSRequestorAuthenticationInd
- MasterCard merchant fraud rate
- Absence of score
- Prior Reference Transaction is retrieved
- Compare amount of prior and subsequent transaction
- Compare currency of prior and subsequent transaction
- MasterCard risk data – MasterCard “recommendation” and “reason code 1”
- CB recommendation – “cbAction” data
- VISA DAF fields ; authPayProcessReqInd, authPayCredStatus and dafAdvice
- VISA VPP indicator
- FIDO assertion or attestation control
- PAN is card virtual ; boolean
- Issuer Maintenance Mode activation on ACS platform ; boolean
Some criterion values depend on the transaction context. Others, like threshold are variable defined by the Bank in the rules engine module.
2.1.2.2 Rules
A rule is a list of operands which apply to criterion to make an action.
Available Operands are:
- Equals
- Lower [or equals]
- Greater [or equals]
- And
- Or
- Boolean
- In
Actions are:
- Fix decision value for a specific reason
- Continue to next rules
2.1.2.3 Rules set
A rules set is a list of rules defined in an established order which defines the priority of the rules and the strategy of the bank to take a SCA Decision.
Figure 4 - Example of Rules Profile
Rules set can be defined on Service, Issuer or Sub-Issuer Level. However, only one rules profile can be defined for a given Bank. If a sub-Issuer doesn’t have profile defined then the profile of its Issuer will be applied.
Specific rules set could also be defined based on optional information: 3DS Protocol Version (2.2 or 2.3.1), Network (VISA, MasterCard, CB, …), location (Merchant Country in or outside EEA) and deviceChannel (Browser Base, App base, 3RI)
In case of lot of rules set definition with intersection, the rules to apply is retrieved base on the priority order below:
- service: required
- issuer: required
- subIssuer: optional
- location: (Merchant Country - EEA) optional
- Network optional
- Protocol Version optional
- deviceChannel: optional
2.1.2.3 Rules configuration
The bank can modify the existing rules directly via the API and ACS back-office or via integration project depending on the complexity of the change expected.
2.2 PSD2 RTS requirements
SCA exemptions are based on the level of risk, amount, recurrence and the payment channel used for the execution of the payment. These exemptions allow PSPs to achieve the right balance between convenience of the payment experience and fraud reduction
WL APM includes a Rules engine and Risk-Based Authentication compliant with PSD2 RTS and schemes requirements to check SCA exemptions.
By default, the WL APM module includes the following rules:
- Check acquirer location
- Check amount vs minus threshold (by default 30 euros)
- Check cumulative amount since last SCA (by default 100 euros)
- Check number of transaction since last SCA (by default 5 transactions)
- Check amount vs issuer ETV
- Check RBA risk value (low / medium / high)
- Check if recurrent transaction
- Check Acquirer Exemption
- Check 3RI Use Cases
The following rules are out of the scope of the 1st version of WL APM:
- Check if beneficiary is the payee (out of 3DS scope)
 Figure 5 – Application of PSD2 RTS Rules – arts 16 and 18
Figure 5 – Application of PSD2 RTS Rules – arts 16 and 18
WL APM manages exemptions which apply to 3DS flows. Here are the detailed rules:
Concerned flows | Exemption | Rules | Conditions of the exemption | Implementation |
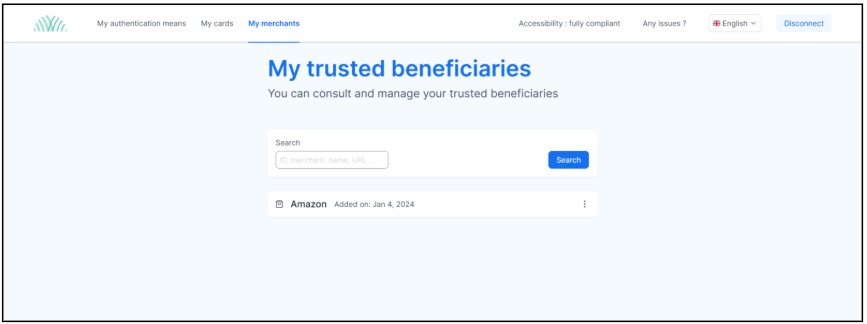
3DS | Art 13 Trusted beneficiaries | SCA applies when the user creates or modifies a list of trusted beneficiaries through the payer’s account servicing PSP | Exemption if the payer initiates a payment transaction and the payee is included in a list of trusted beneficiaries previously created by the payer. | See TML |
3DS | Art 14 Recurring transactions | SCA applies when a payer creates, amends or initiates for the 1st time, a series of recurring transactions with the same amount and with the same payee | Exemption for the initiation of all subsequent payment transactions included in the series of payment transactions | |
3DS | Art 16 Low-value transactions | Exemption of SCA according to the following conditions: | 1 – the amount of remote electronic payment transaction does not exceed EUR 30, AND 2 – the cumulative amount of previous remote electronic payment transactions initiated by the payer since the last application of SCA does not exceed EUR 100, OR 3 – the number of previous remote electronic payment transactions initiated by the payer since the last application of SCA does not exceed 5 consecutive individual remote electronic payment transactions | See low value transaction |
3DS | Art 17 Secure corporate payment processes and protocols | Exemption of SCA in respect of legal persons initiating electronic payment transactions through the use of dedicated payment processes and protocols that are only made available to payers who are not consumers, where the competent authorities are satisfied that those processes or protocols guarantee at least equivalent levels of security to those provided by Directive (EU) 2015/2366 | ||
3DS | Art 18 Transaction risk analysis | SCA exemption if the PSP considers the remote electronic payment as posing low level of risk according to the transaction monitoring mechanisms | 1 – the fraud rate for this type of transaction is equivalent to or below the reference fraud rates specified in the table set out in the annex for “remote electronic card-based payments” and “remote electronic credit transfers” respectively 2 – the amount of the transaction does not exceed the ETV specified in the table set out in the annex 3 – PSP have not identified risky elements further to the real time risk analysis they have done (6 elements to be checked by the scoring tool + 4 risk-based factors to be taken into account) | |
3DS | Art 19 Calculation of fraud rates | For each type of transaction, the PSP shall ensure that the overall fraud rates covering both payment transactions strongly authenticated or exempted are equivalent to or lower than the reference fraud rate for the same type of payment transaction indicated in the table set out in annex. The ETV has to be updated every 90 days | API provided to update the ETV + ETV value history |
3 White & Black lists
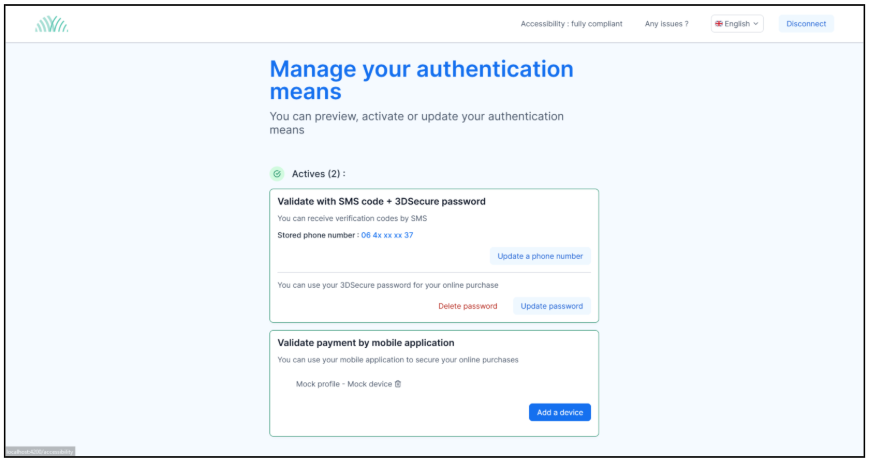
This function allows managing standard fraud prevention lists. You can access it via the navigation banner by selecting the heading <Fraud>.
Fraud is controlled in real time for each transaction thanks to the fraud parameters which have been entered in the ACS3 Back Office.
The available fraud functions on the platform are:
- Cards in white/black lists,
- Cards in exemption lists,
- Blacklisted authentication mean
- IP filters
- Blacklisted merchants (URL, Name, ...)
- Country blacklist (cardholder IP)
- Fraud lists search
3.1 Cards in white/black or exemption lists
This function is used to:
- Search for a whitelist or blacklist card
- Add a card to the blacklist, whitelist or exemption list
- Delete a card from the blacklist or the whitelist.
Business rules :
- When a card is blacklisted, the card is blocked for all authentication requests. A blacklisted card will neither be able to perform a challenge nor participate in frictionless authentication.
- When a card is whitelisted, it benefits from an exemption, allowing it not to be affected by merchant-based, country-based and IP-based blacklists.
- When a card is placed on the exception list, it is identified as such and can therefore have rules specific to the ACS authentication profile.
3.2 Blacklisted means
This function is used to:
- Search for the presence of an authentication mean in the blacklist via the phone number or the e-mail address
- To add an authentication mean in black list
- Delete a blacklisted authentication mean.
Business rules :
- When a mean (phone number or email address) is blacklisted, it is automatically retired from the list of available credentials.
- If the blacklisted credential is the only credential available, the associated authentication method is revoked for the current transaction.
- An authentication mean can be blacklisted for a determined period or indefinitely.
3.3 IP filters
This function allows you to:
- Look for the existence of a IP filter
- Add an IP filter to a blacklist
- Delete an IP filter from the black list.
Business rules :
- If the Cardholder IP address of the transaction is in a blacklisted range, the authentication is declined.
- The IP filter can be applied to the instance, or the issuer and its sub-issuers or to one sub-issuer.
- The IP filter can be limited to an IP address, to an IP range or to an IP address mask.
3.4 Blacklisted merchants
This merchant black list is based on the following information:
- The merchant URL, name, id or domain
- The cardholder IP country who makes his purchase on the merchant website (Geo-location)
- A threshold amount and its direction (>= / <=)
These 3 pieces of information are managed by the rules engine.
The first piece of information is transmitted in the PAREQ or AREQ messages sent by the merchant.
The user can carry out the following actions via the back-office:
- View the blacklisted merchants
- Add a merchant in the black list
- Delete a merchant from the black list
Business rules :
- If the merchant data refers to one of the blacklisted merchant lists, the authentication is declined.
- The Merchant blacklist can be applied to the instance, or the issuer and its sub-issuers or to one sub-issuer.
- The Merchant blacklist can be defined for a merchant URL, merchant name or a merchant domain.
3.5 Country Blacklist
This function allows:
- Access to the blacklist of countries (IP cardholder)
- Add a country to the blacklist
- To modify the pivotal amount above which transactions are refused
- To delete a country from the black list.
Business rules :
- When a country is blacklisted, all transactions from that country are rejected if the amount of the transaction is greater than the amount set for the country.
- The country is detected from the IP address of the cardholder.
- The country blacklist can be applied to the instance, or the issuer and its sub-issuers or to one sub-issuer.
4 Merchants List
On APM rules engine is possible to define a rule for a limited list of merchants. To do that, the rule must include an operator which checks Merchant inclusion in Issuer’s List Merchant for a specific category flag.
The check is done based on the merchant name, field “merchantName” in protocol 2. The name of the merchant defined in the ACS list must be strictly equals to the name provided in the 3DS.
The list could be defined on Instance, Issuer or Sub-Issuer Level.
The list of merchant is limited to 500 merchants.
Each merchant is included in specific categories. A merchant could be flagged in 1 to N categories.
The available categories are:
- Secure Corporate
- Trusted Beneficiaries ACS
- Trusted Beneficiaries 3DS Server
- Delegated Authentication
- TRA
- Risk
- Level 1 to 5
The APM rule condition will be for example:
merchantName ∈ {Merchants List flagged “Secure Corporate”}
Merchants List could be managed in ACS BO or via standard Public RBA API
5 Exonerating hint
If an external scoring platform is configured for a Customer, then the logic comes as described below:
- During AReq processing, a Scoring request is sent to scoring platform
- After the ARes message (Frictionless) or RRes message (Challenge), a Notification request (Advice) is sent to scoring platform
A score (authScore) and a decision (authIndicator) are returned in score response message.
It is also possible for an external scoring platform to provide an RBA reason using generic field exoneratingHint.
If the exonaratingHint contains an existing valid Reason (cf. reason types list)
then APM could returns this value to ACS platform which triggers the transStatus and transStatusReason values accordlingly.
APM must be configured with a single rule to apply the Scoring recommentation :
- decision = EXTRBADECISION
- reason = EXT_RBA

The APM configuration to handle the exoneratingHint field and the overriding logic is defined in the table below:
Name | Condition | Exonerating Hint | ReasonType |
Use case 1 | rbaReason = EXT_RBA and exoneratingHint = HIGH_SCORE and rbaDecision = SCA | HIGH_SCORE | HIGH_SCORE |
Use case 2 | rbaReason = EXT_RBA and exoneratingHint = HIGH_SCORE and rbaDecision = FRICTIONLESS | HIGH_SCORE | EXT_RBA |
Use case 3 | rbaReason = EXT_RBA and exoneratingHint = ANY_UNKNOWN_LABEL and rbaDecision = FRICTIONLESS | ANY_UNKNOWN_LABEL | EXT_RBA because ANY_UNKNOWN_LABLE is a not included in authorized RBA reasons list |
In summary, if APM is configured to use the Scoring platform decision as received, then the rbaReason returned to ACS must be the externalRBA Reason, i.e., if rbaReason = EXT_RBA