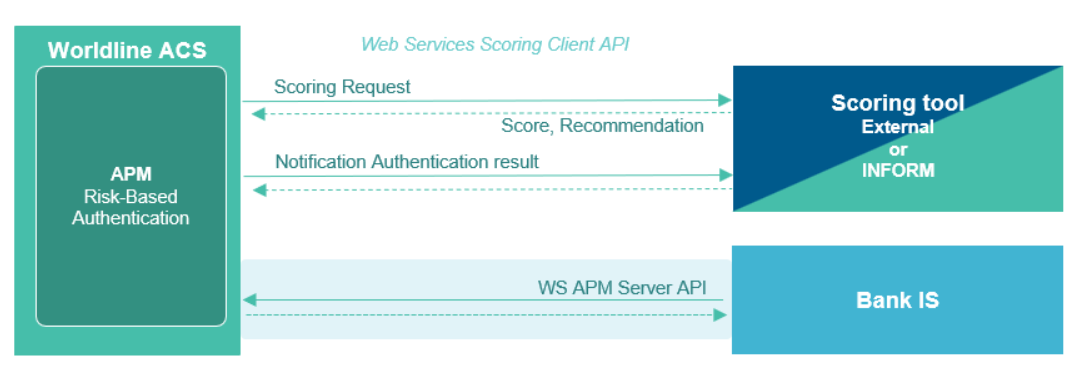
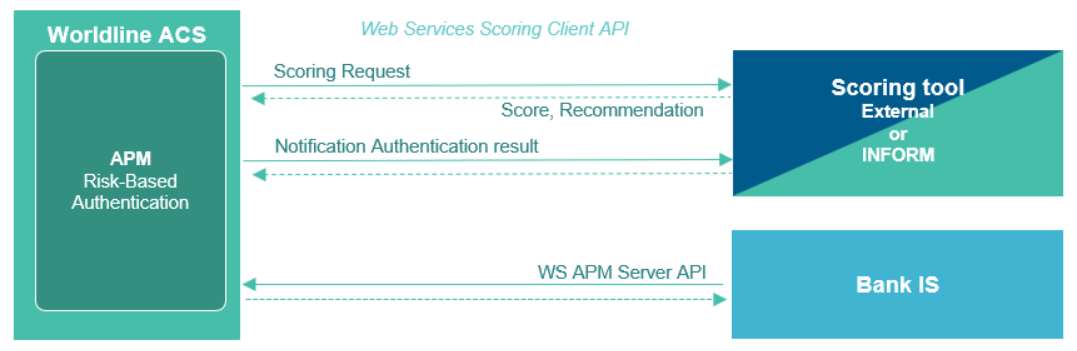
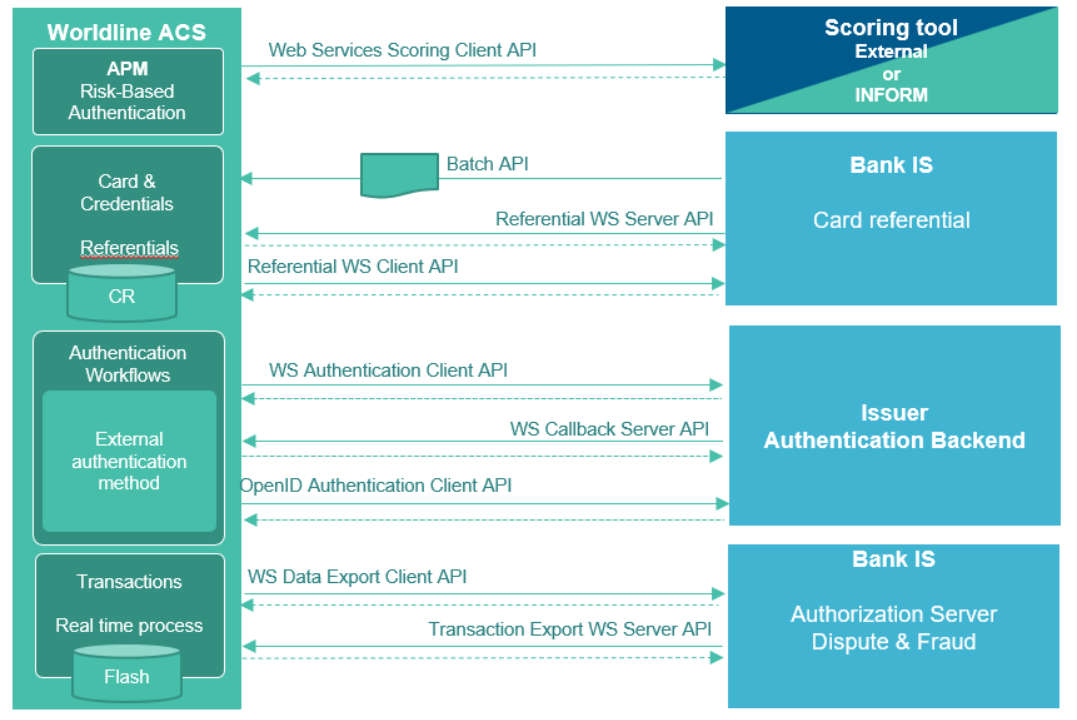
Authentication OpenID WS Client
This document describes the OpenID 1.0 interfaces exposed by an external authentication platform and expected by Authentication HUB as client server. This document is based on OpenID 1.0 specifications
1. Overview
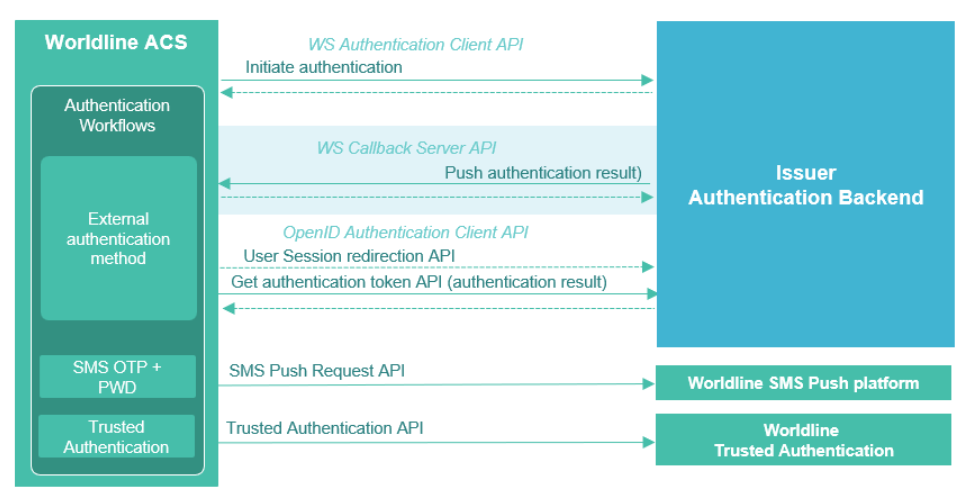
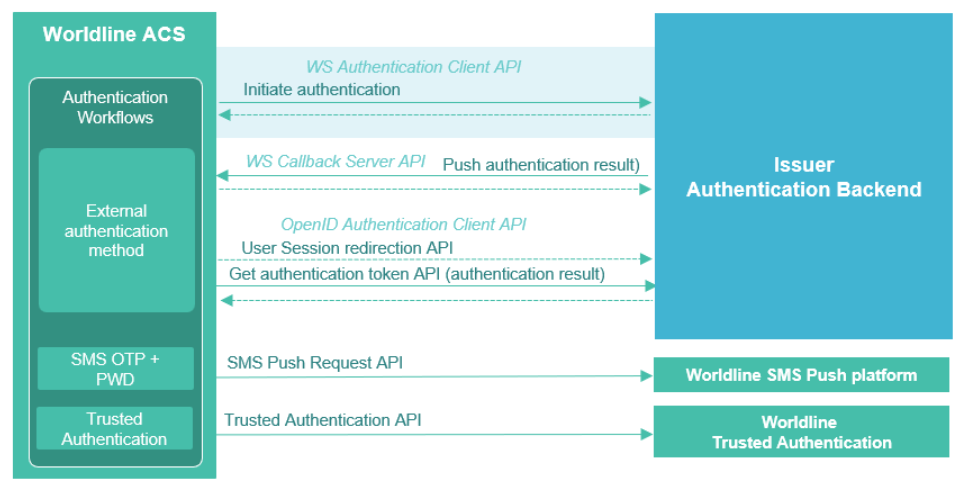
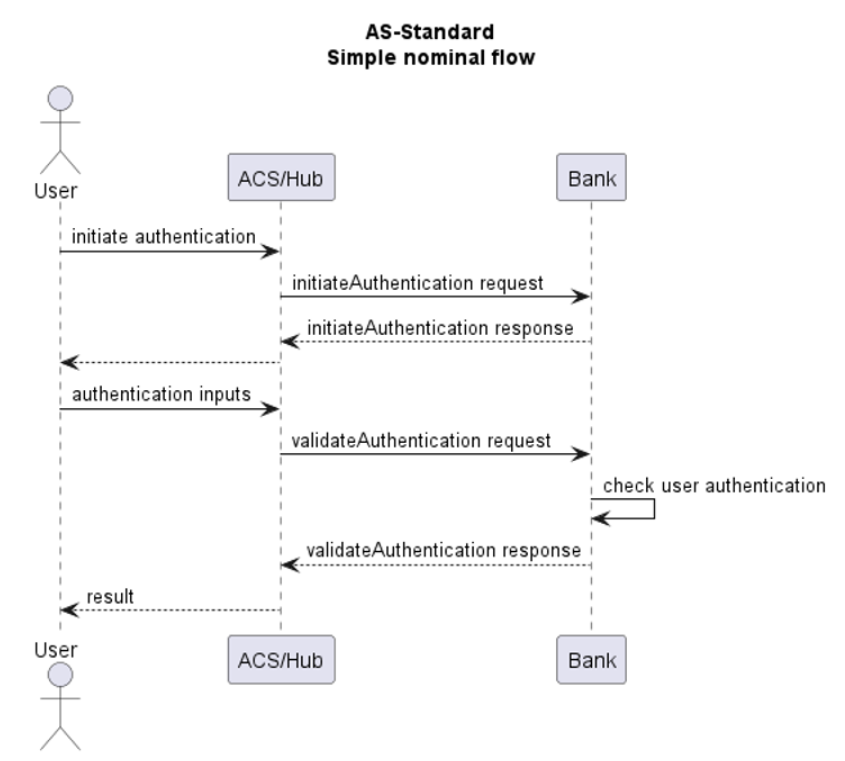
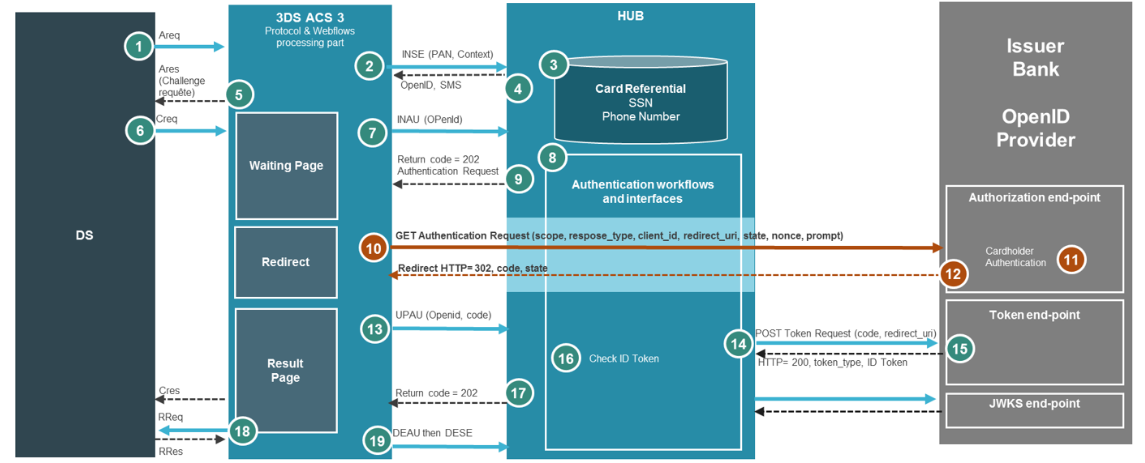
Authentication HUB uses the OpenID Authorization Code Flow to do user authentication during a 3DS request.
The Authorization Code Flow goes through the following steps.
- Client (HUB) prepares an Authentication Request containing the desired request parameters. – STEP 8
- Client (ACS3) sends the request to the Authorization Server. – STEP 10
- Authorization Server (Issuer Bank) authenticates the End-User.– STEP 11
- Authorization Server (Issuer Bank) sends the End-User back to the Client with an Authorization Code. – STEP 12
- Client (HUB) requests a response using the Authorization Code at the Token Endpoint.– STEP 14
- Client (HUB) receives a response that contains an ID Token and Access Token in the response body.– STEP 15
- Client (HUB) validates the ID token and retrieves the End-User's Subject Identifier.– STEP 16
2. Requirement
All following informations should be provided beforehand in order to setup OpenID authentication.
Provided to Authentication HUB by Authorization server:
- Authorization server openid configuration url ( which contains jwks_uri, authorization_endpoint, token_endpoint, should not contain fragment components)
- Client password : client_id and client_secret (RFC6749 section-2.3.1)
- Whether or not authentication data validation is necessary on HUB side
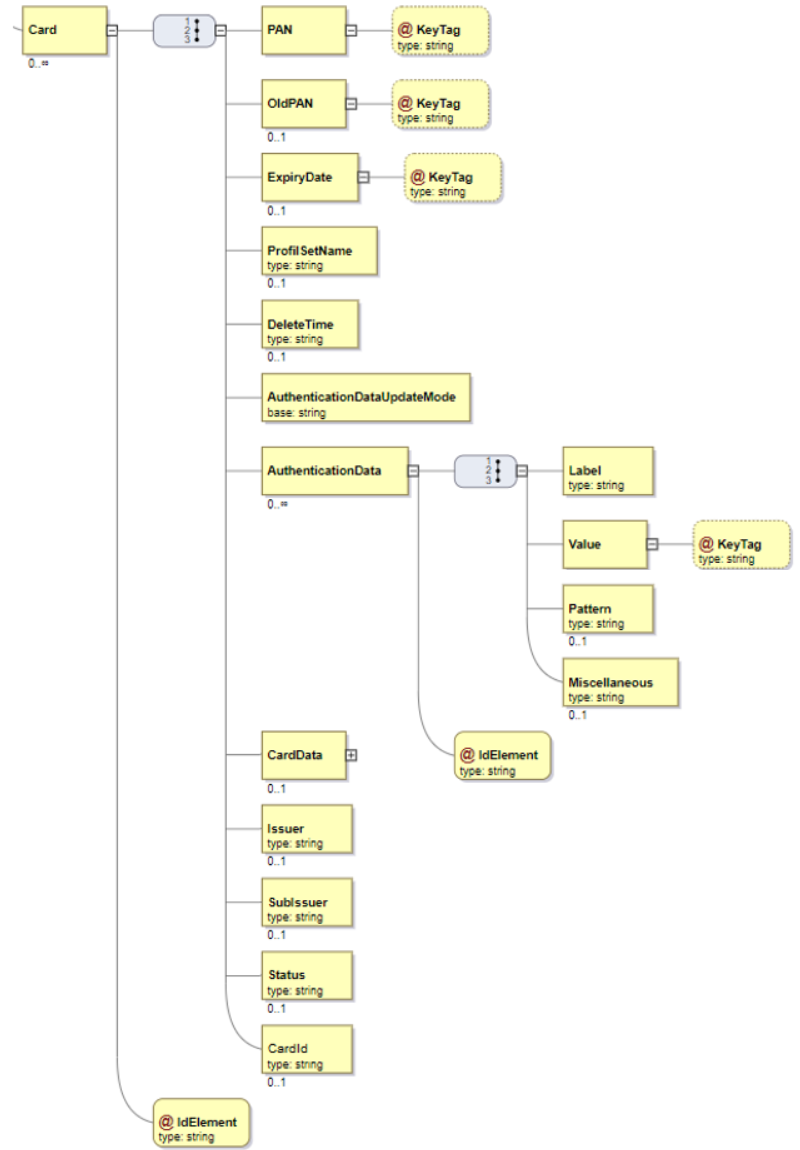
- Authentications data type used for end user authentication (data should be provided in HUB repository database using the credential type 'OPENID')
Provided to Authorization server by Authentication HUB:
- RSA Public key for token encryption (JWE)
3. Connectivity
3.1. Network
All the services are exposed through the HTTPS protocol (RFC 2818) TLS 1. 2.
No HTTP compression (RFC 2616) is activated.
3.2. Security
RSA keys used MUST be 2048 bits or longer. Elliptic curve keys must be long enough to provide a symmetric key equivalent security strength of at least 112 bits (typical EC algorithm key length of 224 bits or longer). Symmetric keys MUST be 128 bits or longer. Hash algorithms used MUST have a digest size of 224 bits or longer.
3.2.1. Signature
Tokens MUST be digitally signed JWTs and must be validated by the receiver using the pre-exchanged signature validation keys. JOSE header kid (RFC 7515) should be used for identifying the key used in all cryptographically secured JWTs. The algorithm used for signing is RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5 using SHA-256 for JWS (RS256 value for alg header field) and RSAES OAEP using default parameters for JWE (RSA-OAEP value for alg header field). The public key for the kid value should be available for validation in a JWKS endpoint (RFC7517).
By default, the authentication HUB will call JWKS endpoint in these cases:
- Hub applications start
- New kid value provided by authorization server (signature certificates renewal for example)
- Once per day to check JWKS endpoint availability
The public certificates will be stored in a memory cache in order to avoid calling JWKS endpoint for each transaction. If the server maintainer wants the Hub to make a call for each transaction, it can request it.
3.2.2. PKCE
OAuth 2.0 provides a version of the Authorization Code Flow which makes use of a Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE).
Usage of PKCE is optional and must be configured during project phase.
The PKCE introduces a secret created by the HUB that can be verified by the authorization server; this secret is called the Code Verifier. Additionally, the HUB creates a transform value of the Code Verifier called the Code Challenge and sends this value over HTTPS to retrieve an Authorization Code. This way, a malicious attacker can only intercept the Authorization Code, and they cannot exchange it for a token without the Code Verifier.
A Code Verifier is generated by HUB for each Oauth transaction, it is a high-entropy cryptographic random with a minimum length of 43 characters.
The Code Challenge is calculated by hashing the Code Verifier in SHA256 then encoding the hash in B64.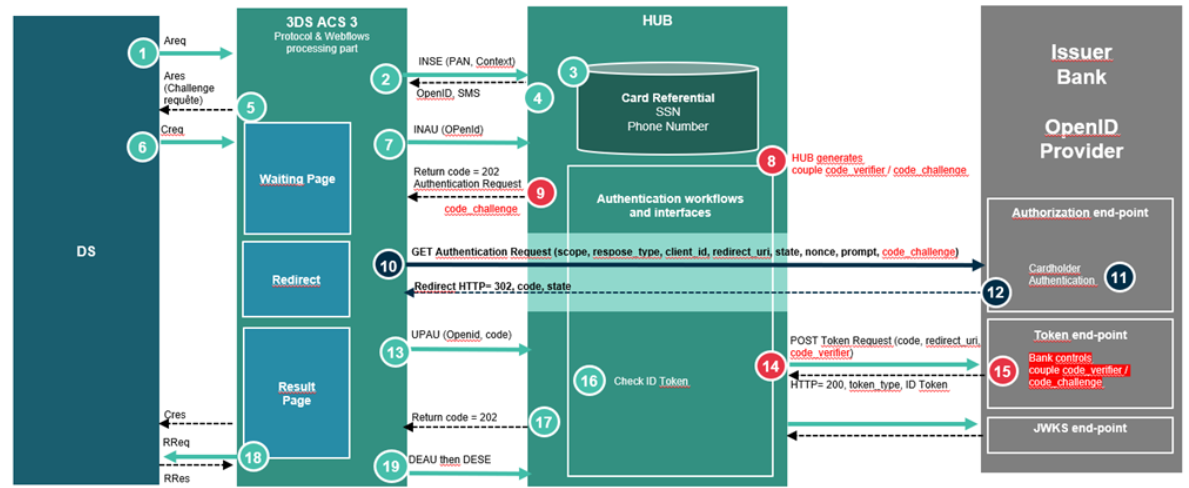
3.2.3. Encryption
Encryption of OIDC Tokens is mandatory for Token with authentication data. The ID Token from the Authorization Server must be first signed by one of the signing private keys and then encrypted using the Authentication HUB public encryption key. In other words, the Token is first secured with JWS and then with JWE to create a nested JWT as described in the OIDC Core specification (section 10). For this to be possible the Authentication HUB needs to have an asymmetric encryption key.
The encryption algorithm used is RSAES OAEP using default parameters (RS256 value for alg header field).
4. OpenID Connect methods
4.1. Authorization endpoint
The Authorization Endpoint performs Authentication of the End-User. This is done by sending the User Agent to the Authorization Server’s Authorization Endpoint for Authentication and Authorization, using request parameters defined by OAuth 2.0 and additional parameters and parameter values defined by OpenID Connect.
4.1.1. Request
Authentication endpoint should support POST and GET. ACS client will use GET method to send the request.
Parameters
| Field | Value | Mandatory | Format | Comment |
| scope | openid | X | ||
| response_type | code | X | ||
| client_id | X | Variable, maximum 255 characters / String | Client identifier retrieved during registration | |
| redirect_uri | X | String of 1 to 2048 characters | ACS redirect uri | |
| state | X | MUST contain at least 128 bits of entropy (for example at least 22 random characters A-Z, a-z, 0-9). | ||
| Nonce | X | MUST contain at least 128 bits of entropy (for example at least 22 random characters A-Z, a-z, 0-9). | ||
| Prompt | login | X | ||
| ui_locales | Format described in rfc5646 | End user language preference tags (BCP 47) | ||
| transaction_id | X | Unique Transaction identifier Length: 36 characters | UUID HUB authentication id | |
| session_id | Unique Transaction identifier Length: 36 characters | HUB / ACS session id | ||
| payee | Areq.merchantName Optional for NPA | |||
| amount | Amount without exponent | Areq.purchaseAmount Optional for NPA | ||
| currency_code | Currency code on 3 digits as defined in ISO 4217 | Areq.purchaseCurrency Optional for NPA | ||
| currency_exponent | Minor units of currency as specified in the ISO 4217 currency exponent | Areq.purchaseExponent Optional for NPA | ||
| trusted_enrollment_request | Contains trusted beneficiary consent information | Boolean | ||
| login_hint | Hint to the Authorization Server about the login identifier the End-User might use to log in (if necessary) | String | ||
| code_challenge | C (mandatory for PKCE) | PKCE challenge code | B64 encoding of SHA256 of code verifier | |
| code_challenge_method | C (mandatory for PKCE) | Constant equals S256 when code verifier transformation method is SHA256 | S256 |
Sample
GET /authorize?
scope=openid
&response_type=code
&client_id=s6BhdRkqt3
&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fclient.example.org%2Fcb
&state=af0ifjsldkj
&nonce= n-0S6_WzA2Mj
&prompt=login
&transaction_id=3a6f4695-e791-45c4-9a9f-95bf0e416346
&payee=merchant
&amount=10000
¤cy_code=978
¤cy_exponent=2
&trusted_enrollment_request=true
&login_hint=571a48b12
&code_challenge=E9Melhoa2OwvFrEMTJguCHaoeK1t8URWbuGJSstw-cM
&code_challenge_method=S256
Host: server.example.com
4.1.2. Response
Response should return a 302 Found HTTP code even if error fields are non-empty.
Response without error:
| Field | Value | Mandatory | Format | Comment |
| code | X | Code from authentication Response (could be null or not provided see remark below) | ||
| state | X | MUST contain at least 128 bits of entropy (for example at least 22 random characters A-Z, a-z, 0-9). | Repeated from request |
If “code” field is null or not provided then the use case corresponds to a user cancellation on authorization server.
If authentication fails, the field error must be set to “access_denied” and an error_description can be provided to distinguish the reason of this functional authentication failure.
Response with error:
| Field | Value | Mandatory | Format | Comment |
| state | X | MUST contain at least 128 bits of entropy (for example at least 22 random characters A-Z, a-z, 0-9). | Repeated from request | |
| error | X | See error code below | ||
| error_description | Trace id in case of analysis requested or reason of authentication failure. |
Errors
| Error | Description |
| invalid_request | The request is missing a required parameter, includes an invalid parameter value, includes a parameter more than once, or is otherwise malformed. |
| unauthorized_client | The client is not authorized to request an authorization code using this method. |
| access_denied | The resource owner or authorization server denied the request. |
| unsupported_response_type | The authorization server does not support obtaining an authorization code using this method. |
| invalid_scope | The requested scope is invalid, unknown, or malformed. |
| server_error | Internal server error |
| temporarily_unavailable | The authorization server is currently unable to handle the request |
Error descriptions
error_description is a free value, but Hub will interpret differently the following values in case of error = access_denied:
| error_description | Description |
| Auth_blocked | Authentication is blocked. |
| Auth_failed | Authentication failed. |
| Auth_expired | Authentication is expired. |
Samples
Success:
HTTP/1.1 302 Found Location: https://client.example.org/cb? code=SplxlOBeZQQYbYS6WxSbIA &state=af0ifjsldkj
Technical Error:
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Location: https://client.example.org/cb?
error=invalid_request
&error_description=Unsupported%20response_type%20value
&state=af0ifjsldkj
Authentication Failure:
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Location: https://client.example.org/cb?
error=access_denied
&error_description=Auth_failed
&state=af0ifjsldkj
4.2. Token endpoint
To obtain an Access Token, an ID Token, and optionally a Refresh Token, the HUB (Relying Party - Client) sends a Token Request to the Token Endpoint to obtain a Token Response, as described in Section 3.2 of OAuth 2.0 [RFC6749], when using the Authorization Code Flow.
4.2.1. Request
To exchange the authorization code for an access token, HUB client makes a POST request to the service’s token endpoint.
Headers
| Field | Value | Comment |
| Content-Type | application/x-www-form-urlencoded | |
| Authorization | Basic client_id:client_secret | string “client_id:client_secret” encoded in Base64 |
Parameters
| Field | Value | Mandatory | Format | Comment |
| grant_type | authorization_code | X | ||
| code | X | String | authorization code received from the authorization server | |
| redirect_uri | X | String of 1 to 2048 characters | ACS redirect uri (same as authorization request) | |
| code_verifier | PKCE code verifier | high-entropy cryptographic random with a minimum length of 43 characters and a maximum length of 128 characters |
Sample
POST /token HTTP/1.1
Host: server.example.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Authorization: Basic czZCaGRSa3F0MzpnWDFmQmF0M2JW
grant_type=authorization_code
&code=SplxlOBeZQQYbYS6WxSbIA
&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fclient.example.org%2Fcb
&code_verifier=0MF7_qn397NQ_c1cnJkIB4tKPZrWXX0yAFCWFiYw_VA
4.2.2. Response
After receiving and validating a valid and authorized Token Request from the HUB, the Authorization Server returns a successful response that includes an ID Token and an Access Token.
Parameters
Response should return a 200 http code for success (for error http code see below).
Response without error:
| Field | Value | Mandatory | Format | Comment |
| access_token | X | String | Not used by the HUB | |
| expires_in | Integer | Not used by the HUB | ||
| token_type | Bearer | X | ||
| id_token | X | String | JWT token (see below for description) |
Response with error:
| Field | Value | Mandatory | Format | Comment |
| error | String | See error code below | ||
| error_description | String | Trace id in case of analysis requested |
4.2.2.1. ID Token without authentication data
JWS
| JWS Header | ||||
| Field | Value | Mandatory | Format | Comment |
alg
| RS256 | X | RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5 using SHA-256 | |
| kid | X | String | Kid should be in server JWKS url endpoint | |
| JWS Payload | ||||
| iss | X | String | Issuer identifier url (without uri) | |
| sub | X | String | Subject identifier (unique for the transaction) | |
| aud | X | String | client ID (same as provided by client in authorization request) | |
| exp | X | NumericDate (RFC7519) | current time + 5mn | |
| iat | X | NumericDate (RFC7519) | time at which the token was generated | |
| auth_time | X | NumericDate (RFC7519) | time when the authentication occurred | |
| nonce | X | String | same value as in previous messages | |
| JWS Signature | ||||
4.2.2.2. ID Token with authentication data
The ID Token is a nested JWT (JWE containing a JWS, first signed and then encrypted JWT containing information about the end user that authenticated) In order to protect authentication data, the token should be encrypted with the public key of the Authorization server.
HUB will generate a privet/public key pair (format RSA AES 256). Only public key is shared with the Issuer Bank Authorization Server.
JWE
| JWE Header | ||||
| Field | Value | Mandatory | Format | Comment |
alg
| RSA-OAEP | X | RSAES OAEP using default parameters | |
| enc | A128GCM | X | ||
| kid | X | String | Kid should be in server JWKS url endpoint | |
| JWE Ciphertext | ||||
| JWS token (see below) | ||||
JWE also contain Encrypted Key, Initialization Vector and Tag, descripted in JWE specification. (https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-jose-json-web-encryption-40)
JWS
| JWS Header | ||||
| Field | Value | Mandatory | Format | Comment |
alg
| RS256 | X | RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5 using SHA-256 | |
| kid | X | String | Kid should be in server JWKS url endpoint | |
| JWS Payload | ||||
| iss | X | String | Issuer identifier url | |
| sub | X | String | Subject identifier (unique for the transaction) | |
| aud | X | String | client ID | |
| exp | X | NumericDate (RFC7519) | current time + 5mn | |
| iat | X | NumericDate (RFC7519) | time at which the token was generated | |
| auth_time | X | NumericDate (RFC7519) | time when the authentication occurred | |
| nonce | X | String | same value as in previous messages | |
| data_type_1 | X | String | Authentication data type, possible value: SSN,DDN,PWD, … | |
| data_value_1 | X | String | Authentication data value | |
| data_type_2 | String | Authentication data type, possible value: SSN,DDN,PWD, … | ||
| data_value_2 | String | Authentication data value | ||
| data_type_3 | String | Authentication data type, possible value: SSN,DDN,PWD, … | ||
| data_value_3 | String | Authentication data value | ||
| data_type_4 | String | Authentication data type, possible value: SSN,DDN,PWD, … | ||
| data_value_4 | String | Authentication data value | ||
| data_type_5 | String | Authentication data type, possible value: SSN,DDN,PWD, … | ||
| data_value_5 | String | Authentication data value | ||
| JWS Signature | ||||
Authentication data claims
Authentication data used for end user authentication on HUB side are stored in “data_type_X” and “data_value_X”. Only “data_type_1” and “data_value_1” are mandatory for authentication. If authentication servers require more security, up to five authentication data could be sent to the HUB for check. Authentication data type should be exchanged beforehand between authorization server and HUB client.
Sample
data_type_1 : DDN
data_value_1 : 10/03/1980
data_type_2 : PWD
data_value_2 : totopwd
Errors
| HTTP Code | Error | Description |
| 400 | invalid_request | The request is missing a required parameter, includes an invalid parameter value, includes a parameter more than once, or is otherwise malformed. |
| 400 | invalid_grant | The provided authorization grant (e.g., authorization code, resource owner credentials) is invalid, expired, revoked does not match the redirection URI used in the authorization request, or was issued to another client. |
| 400 | unauthorized_client | The authenticated client is not authorized to use this authorization grant type. |
| 400 | unsupported_grant_type | The authorization grant type is not supported by the authorization server. |
| 401 | invalid_client | Client authentication failed |
Other HTTP code should be treated as an unknown error.
Samples
Success:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
{
"access_token": "SlAV32hkKG",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"refresh_token": "8xLOxBtZp8",
"expires_in": 3600,
"id_token": " eyJhbGciOiJSU0EtT0FFUCIsImVuYyI6IkEyNTZHQ00ifQ.
OKOawDo13gRp2ojaHV7LFpZcgV7T6DVZKTyKOMTYUmKoTCVJRgckCL9kiMT03JGe
ipsEdY3mx_etLbbWSrFr05kLzcSr4qKAq7YN7e9jwQRb23nfa6c9d-StnImGyFDb
Sv04uVuxIp5Zms1gNxKKK2Da14B8S4rzVRltdYwam_lDp5XnZAYpQdb76FdIKLaV
mqgfwX7XWRxv2322i-vDxRfqNzo_tETKzpVLzfiwQyeyPGLBIO56YJ7eObdv0je8
1860ppamavo35UgoRdbYaBcoh9QcfylQr66oc6vFWXRcZ_ZT2LawVCWTIy3brGPi
6UklfCpIMfIjf7iGdXKHzg.
48V1_ALb6US04U3b.
5eym8TW_c8SuK0ltJ3rpYIzOeDQz7TALvtu6UG9oMo4vpzs9tX_EFShS8iB7j6ji
SdiwkIr3ajwQzaBtQD_A.
XFBoMYUZodetZdvTiFvSkQ"
}
Error:
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Content-Type: application/json
{
"error": "invalid_request"
}
4.2.2.3. Token Response Validation
This token response needs to be checked by us to be sure that :
- Authentication is successful,
- Authentication is performed by the expected Cardholder.
In addition to the OpenID Connect standard validation (section 3.1.3.5), the cardholder identifier(s) must be checked with data known by HUB.
If the ID Token doesn’t contain authentication data, the Subject Identifier included in response message (field sub) must contain the expected cardholder identifier stored in the HUB repository.
The HUB platform can manage 3 different types of identifier :
- SSN - Social Security number
- OPENID – Dedicated cardholder identifier for OpenID authentication method
- CARDHOLDERID – Cardholder identifier
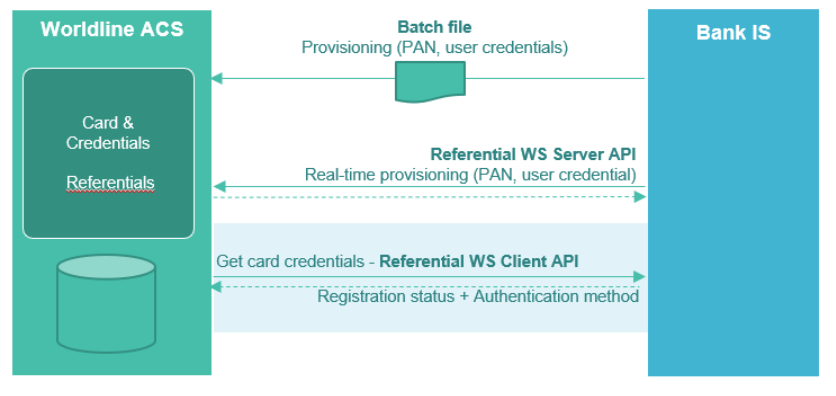
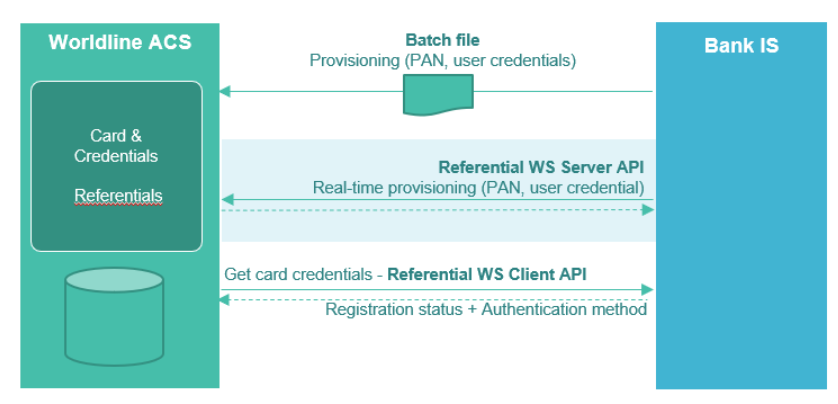
An Issuer Bank configuration is set during Project Phase to define what kind of identifier will be used. The corresponding information must be provided by Bank IS either by Referential Batch File or Web services.
The Subject Identifier is compared to data stored in card repository on HUB side. If it doesn’t match, the HUB will return “authentication failed” status to the ACS application.
If ID Token contains authentication data, in addition to verifying Subject Identifier, the authentication data are compared to data stored in card repository on HUB side. If they don’t match, the HUB will return “authentication failed” status to ACS application.
Currently supported authentication data types are:
- SSN
- DDN (birth date, formatted as “dd/MM/yyyy”)
- PWD (password)
- CARDHOLDERID
4.3. JWKS endpoint
4.3.1. Frequency of requests
The HUB will keep the signing keys in cache session with the corresponding kid value.
A call to the JWKS endpoint is done to retrieve the public key only in the following cases:
- On each restarting the application,
- On each renewing of the public key; when a new “kid” value is returned by OpenID Provider,
- Once a day to check the availability of the service.
4.3.2. Rotation of Asymmetric Signing Keys
Rotation of signing keys must be done every 2 years with the following approach.
The Bank OpenID Provider publishes its keys in a JWK Set at its jwks_uri location and includes the kid of the signing key in the JOSE Header of each message to indicate to the verifier which key is to be used to validate the signature.
Keys can be rolled over by adding new keys to the JWK Set at the JWKS endpoint.
The signer (OpenID provider) can begin using a new key at its discretion and signals the change to the verifier (HUB) using the kid value.
The HUB knows to go back to the jwks_uri location to re-retrieve the keys when it sees an unknown kid value.
The JWK Set document at the jwks_uri SHOULD retain recently decommissioned signing keys for a reasonable period of time to facilitate a smooth transition.
4.4. Provider Configuration endpoint
For details about the Provider Configuration endpoint implementation, see OpenID Connect Discovery documentation.
The claims used by the Authentication Hub are:
- issuer
- authorization_endpoint
- token_endpoint
- jwks_uri
All these claims are necessary. Any additional claim will be ignored.
Answer sample:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
{
"issuer": "https://server.example.com",
"authorization_endpoint": "https://server.example.com/connect/authorize",
"token_endpoint": "https://server.example.com/connect/token",
"jwks_uri": "https://server.example.com/jwks.json"